The adoption of sustainable agriculture is critical in addressing growing global environmental concerns. Africa, as the continent most likely to be impacted most by climate change, must take a stand in support of green initiatives. Given that agriculture is both the primary source of food and the primary source of income for most of the continent's population, it must be safeguarded for the continent's long-term stability. It is estimated that 65% of Africans engage in subsistence farming, and agriculture accounts for a large portion of the continent's GDP.
Furthermore, customer preferences are changing, and more buyers are concerned about the environmental impact of the products they buy and want to know how their favourite purchases ended up in their homes. In the case of agricultural products, this necessitates improved traceability from farm to table.
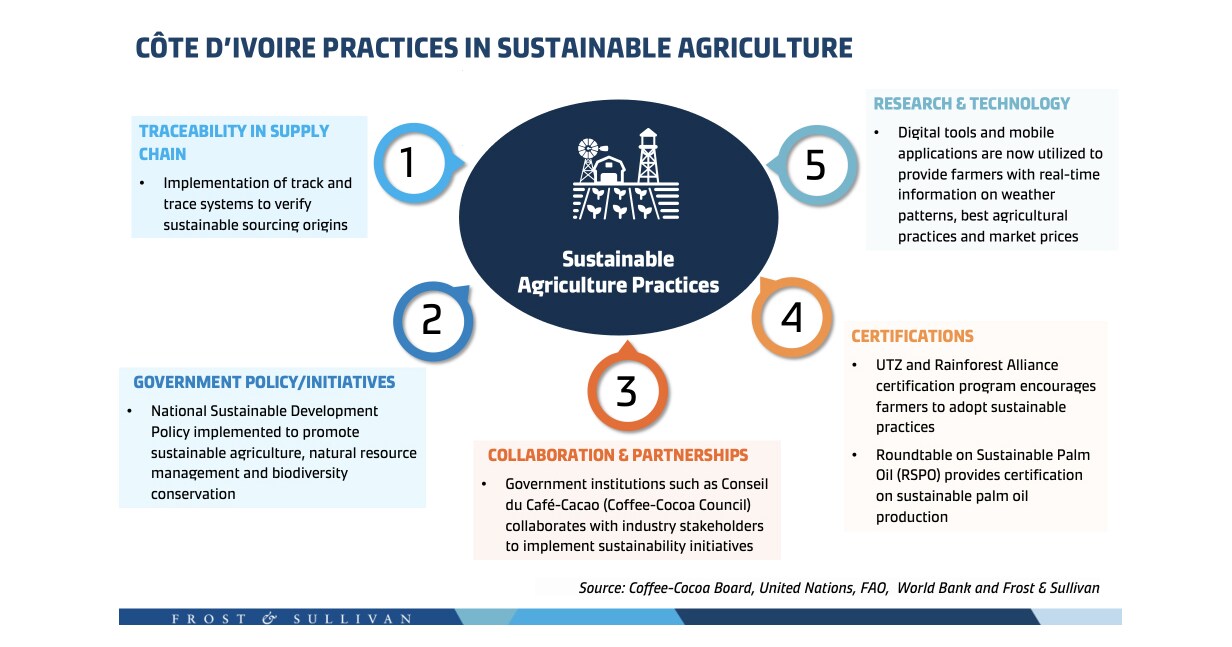
In this article, we will look at Ivory Coast as an example. The West African country is a major global exporter of agricultural commodities such as cocoa, palm oil, bananas, and cashews. Agriculture is vital to the country's economy, accounting for approximately 21.2% of GDP and employing two-thirds of the active working population.
Sustainability in agriculture
However, there are several significant environmental challenges that threaten Cote d'Ivoire's ability to maintain high levels of agricultural production. Environmental degradation, rising temperatures, and prolonged droughts all contribute to the country's vulnerability to climate change. The situation is exacerbated by the fact that agricultural activities account for 12% of the country's greenhouse gas emissions.
As a result, a variety of stakeholders, including government agencies, private businesses, and non-governmental organizations, have taken the lead in promoting sustainable agricultural practices. They are concentrating their efforts on investments and education that prioritize understanding of the long-term environmental, social, and economic sustainability of Ivory Coast agriculture. Furthermore, international markets such as the European Union are increasingly considering cocoa production sustainability as a key factor in deciding where the commodity is sourced.
Traceability as part of promoting sustainability in agriculture
As the world's largest cocoa producer, Ivory Coast has implemented numerous sustainable agricultural practices such as organic farming, agroforestry, efficient water management, and integrated pest management.
The cocoa industry has adopted certification and traceability to provide evidence to the entire value chain. Traceability entails tracking and tracing produce from farmer to consumer, allowing for transparency, sustainability, and social responsibility throughout the value chain. With visibility at all levels, it is easier to identify areas for improvement in the supply chain.
So far, Cote d'Ivoire has reaped numerous benefits from increased traceability. Where, however, are the opportunities for farmers, produce off-takers, and other value-chain players?
Four opportunities for traceability in agricultural sourcing
- Farm-Level Traceability: This is where stakeholders gather information about the farm's production practices, such as land use, cultivation methods, pesticide, and fertilizer use, and even labour practices.
- Supply Chain Integration: Traceability requires collaboration and integration among various stakeholders in the supply chain so that everyone may obtain the essential information. Traceability data is accurately collected and shared across the supply chain thanks to the continuous flow of information enabled by supply chain integration.
- Risk Management and Quality Control: Traceability enables stakeholders to proactively manage risk and control the quality of the produce that reaches the market by identifying and mitigating potential risks such as contamination or noncompliance with regulations.
- Market Access and Consumer Demand: As consumer demand for transparency grows, businesses that can provide verifiable traceability information on sustainable practices throughout the value chain will have a competitive advantage in accessing premium markets and meeting the demands of socially responsible buyers.
The future of sustainable agriculture sourcing is in traceability.
In conclusion, as the world attempts to develop innovative ways to ensure sustainability across all industries, traceability holds the promise of a greener future for agriculture. It will establish a virtuous cycle in which sustainable practices improve consumer trust and demand for ethically sourced products.
未来,您想随时了解必读行业趋势吗?
您已经完成了,欢迎“登船”!
很抱歉,发送您的联系请求时出现问题。
请查看表单字段,确保所有已正确填写所有必填信息。如果问题仍然存在,请联系我们的支持团队以获得进一步的帮助。
未来,您想随时了解必读行业趋势吗?
使用此表格注册,即可直接在您的邮箱中接收我们的洞察见解,进入一个真正的综合物流世界。简单操作,即从我们为您量身定做的精选文章中获得启发,了解相关行业洞察信息。您可以随时取消订阅。
I agree to receive logistics related news and marketing updates by email, phone, messaging services (e.g. WhatsApp) and other digital platforms, including but not limited to social media (e.g., LinkedIn) from A. P. Moller-Maersk and its affiliated companies (see latest company overview). I understand that I can opt out of such Maersk communications at any time by clicking the unsubscribe link. To see how we use your personal data, please read our Privacy Notification.
By completing this form, you confirm that you agree to the use of your personal data by Maersk as described in our Privacy Notification.













